Comprehensive Overview: What is Porosity in Welding and Just How to stop It
Wiki Article
The Science Behind Porosity: A Comprehensive Guide for Welders and Fabricators
Recognizing the intricate mechanisms behind porosity in welding is important for welders and producers making every effort for flawless workmanship. From the structure of the base materials to the details of the welding procedure itself, a wide variety of variables conspire to either worsen or reduce the existence of porosity.Understanding Porosity in Welding
FIRST SENTENCE:
Exam of porosity in welding reveals important insights into the integrity and top quality of the weld joint. Porosity, defined by the existence of cavities or voids within the weld steel, is a typical issue in welding procedures. These voids, if not correctly resolved, can jeopardize the architectural stability and mechanical residential properties of the weld, causing potential failures in the ended up item.
To find and measure porosity, non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic screening or X-ray evaluation are frequently utilized. These methods enable the identification of inner problems without endangering the stability of the weld. By examining the size, shape, and distribution of porosity within a weld, welders can make enlightened decisions to boost their welding procedures and attain sounder weld joints.
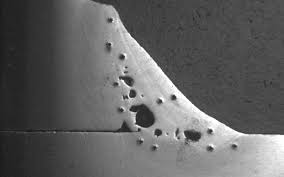
Elements Influencing Porosity Formation
The event of porosity in welding is affected by a myriad of elements, ranging from gas securing performance to the ins and outs of welding specification setups. One important element adding to porosity development is poor gas shielding. When the securing gas, generally argon or carbon dioxide, is not effectively covering the weld pool, atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen can contaminate the molten steel, bring about porosity. Furthermore, the cleanliness of the base products plays a substantial role. Impurities such as rust, oil, or wetness can vaporize throughout welding, developing gas pockets within the weld. Welding criteria, consisting of voltage, current, travel speed, and electrode type, also impact porosity development. Using incorrect setups can generate too much spatter or warm input, which subsequently can cause porosity. The welding method employed, such as gas steel arc welding (GMAW) or shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), can affect porosity formation due home to variations in warmth distribution and gas insurance coverage. Understanding and managing these aspects are vital for lessening porosity in welding operations.Results of Porosity on Weld Quality
The visibility of porosity likewise damages the weld's resistance to corrosion, as the caught air or gases within the voids can respond with the surrounding setting, leading to degradation over time. In addition, porosity can hinder the weld's capacity to endure pressure or influence, additional threatening the general quality and integrity of the bonded framework. In important applications such as aerospace, automotive, or architectural building and constructions, where safety and durability are extremely important, the detrimental effects of porosity on weld high quality can have severe effects, emphasizing the significance of decreasing porosity via correct welding techniques and procedures.Methods to Reduce Porosity
In addition, using the suitable welding specifications, such as the appropriate voltage, present, and take a trip rate, is important in protecting against porosity. Preserving a consistent arc length and angle throughout welding also helps minimize the probability of porosity.
Using the proper welding method, such as back-stepping or utilizing a weaving motion, can also assist distribute heat uniformly and reduce the chances of porosity development. By carrying out these methods, welders can properly decrease porosity and produce premium bonded joints.
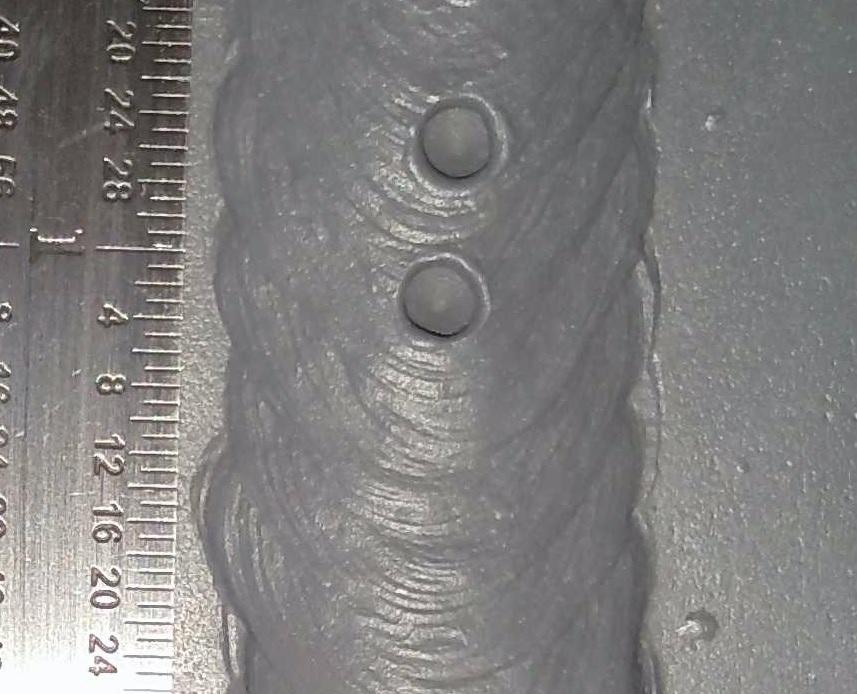
Advanced Solutions for Porosity Control
Executing advanced technologies and innovative methods plays a critical role in attaining exceptional control over porosity in welding procedures. One see here now sophisticated remedy is making use of sophisticated gas blends. Protecting gases like helium or a blend of argon and hydrogen can help in reducing porosity by giving much better arc security and boosted gas protection. Furthermore, using innovative welding techniques such as pulsed MIG welding or customized ambience welding can additionally help minimize porosity issues.One more innovative option involves the usage of advanced welding devices. As an example, making use of tools with integrated functions like waveform control and advanced power sources can improve weld top quality and reduce porosity dangers. The execution of automated welding systems with accurate control over criteria can significantly decrease porosity problems.
Additionally, including innovative tracking and assessment technologies such as real-time X-ray imaging or automated ultrasonic screening can aid in spotting porosity early in the welding process, permitting for instant restorative activities. Overall, integrating these advanced solutions can significantly improve porosity control and enhance the overall quality look at here now of welded elements.
Final Thought
Finally, comprehending the scientific research behind porosity in welding is necessary for welders and producers to create premium welds. By recognizing the aspects influencing porosity formation and implementing strategies to reduce it, welders can enhance the total weld top quality. Advanced options for porosity control can better improve the welding process and ensure a solid and dependable weld. It is necessary for welders to continually inform themselves on porosity and carry out finest practices to accomplish optimum outcomes.Report this wiki page